New story in Health from Time: I’m a Doctor Recovering From COVID-19. I Can’t Get Over the Government’s Callousness for Human Life
Dr. Laura Mulvey, 33, practices emergency medicine at Maimonides Medical Center in Brooklyn, New York. After spending six days receiving treatment in her own hospital, she is now recovering at home from what is presumed to be COVID-19, though her test was inconclusive. What follows is a lightly-edited transcript of her story as told to TIME.
Early on, sometime in February, [COVID-19] was something that people were thinking about. And worried about. Certainly, the worries were not what they are now. But hospital-wise, we had a bit of an earlier jump on it, because we recognized that this was a potential threat. We’re nestled on the intersection of a lot of different neighborhoods — one of which is Brooklyn Chinatown. In February we started having people trickle in who were concerned they had the coronavirus.
We saw these pictures out of China and those health care workers in extensive isolation gear. But I don’t think I anticipated in any way quite the scale that it would be on, and I don’t think all of the problems of the virus were immediately apparent: the long incubation period, which makes it hard to contain, but also the duration of the illness. If someone’s on a ventilator — unless they pass away, they’re probably going to be on that ventilator for a couple of weeks. When you consider your critical resources, you need a lot more than you would initially anticipate.
We realized that the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention criteria for testing were missing the mark. Early on, when we had people coming in concerned that they had coronavirus, they had to have a fever, and a cough, and have traveled from Wuhan. If you’re testing for that, the likelihood that they have COVID is close to 100%. By those guidelines, we were incapable of testing. Nobody had the tests. You had to call the Department of Health to get permission to send a swab. Early on, you’re crippled by your public health response.
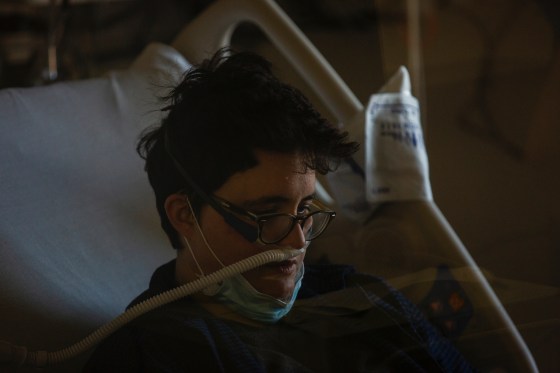
By early March, we were wearing a mask every day at work. Before that, the patients who were COVID rule-outs (patients who potentially have COVID-19) were able to be easily contained in a private room. Usually a negative pressure room. But early March was when things ballooned.
After I got back from a vacation in early March, I worked a couple of emergency department critical care shifts in which I intubated eight COVID rule-outs in the span of two days, around March 14 and 15. Some of them were cardiac arrests. Intubation is probably the most dangerous thing — that, and procedures in the setting of a cardiac arrest. Three days later, I was hanging out at home on my day off, and I just got sick. I had fever and joint pain and a little bit of a sore throat. I was OK for a couple of days, and then shortness of breath like I never had before set in.
I had friends from work, other doctors, calling in and checking on me. By day four, I couldn’t hold a conversation on the phone without coughing and getting really short of breath, so they convinced me to come in to the hospital. My friend, a doctor, picked me up in full PPE (personal protective equipment) in her car, and we drove to the hospital with the windows down.
I was on something called high flow (oxygen). Within a few minutes of being on it, I went from feeling really awful to being like, oh, I feel totally fine now. It really, really helped me. And then I was on azithromycin and hydroxychloroquine.
But it’s not easy being a patient, especially in your own hospital. You’re alone. There are no visitors, except if you’re actively dying or you’re a child. The hospital has this super-eerie feeling — all these elderly people on ventilators, totally alone.
In a way, I had it a lot better than your average patient, because I saw familiar faces every day. It’s a lot of patients that are just behind glass and rooms, and staff that are walking around in protective gear, fearful. If you need something, it’s hard because they have to get all geared up to see you. And you don’t want to ask for anything, because personally I don’t want to put anyone else in any unnecessary risk. I had even a little bit of guilt about, when I was in the hospital, potentially exposing others to the virus who are in and out of your room all day.
The hardest part is not being able to breathe. But also, the unknown. If you could have told me eight days ago, ‘oh, you’re just going to be in the ICU for six days and then you’re going to start feeling better, and you’ll go home,’ it would’ve been a lot easier to deal with. I had worked, and I had seen really sick people, and I’ve seen really sick young people. And I’d intubated a lot of them. Knowing that I had probably taken a bigger viral load hit with all the intubations, that reality is just terrifying. And you’re sitting there, and there’s nothing you can do.
It’s hard to sit in a room alone and not really know which way you’re going to go.
And you don’t have any of your social support. My family actually quarantined upstate, because they live there mostly full-time this year. I was able to FaceTime, which is something probably a lot of elderly people can’t do. My kids, who are 2 and 4, don’t know. They think I was at work. I wore a mask, so they couldn’t really see the whole high-flow setup.
For my wife, her mother died of lung cancer when she was 13, so, this was acutely traumatic for her. She’s isolating upstate and she’s taking care of two kids while she’s really pregnant. I still don’t know how she’s dealing with it. Probably not well.
I managed my own high flow. After six days in the hospital, I was able to get down off the high flow for a long time. The hospital was full, and I was like — you know, I’m just feeling OK enough to manage at home. The hospital is such a sick, ill environment right now, I didn’t want to spend any more time there than I absolutely needed to. I definitely think I have a long way to recover, and certainly my lungs have taken a bit of a hit. It’s going to be a bit of time before I feel like I’m not at risk for regular infections, like pneumonia.
The virus is impacting a subset of people who are infected, but the aftershocks of this are going to be felt in a lot of different areas. The sort of emotional, psychological toll on health care workers will probably lead to people leaving medicine. This idea that — I can’t really adequately say it — that people are dispensable. The government thinks that we can go to work without proper PPE and put our lives at risk. That’s something you can’t really get over — this kind of callousness for human life. I think they should have been trying harder months ago. And there are going to be people who miss their mammograms and get breast cancer. Or they have chest pain and they don’t want to go to the hospital, because they don’t want to get COVID.
They should have identified this early on as a threat to public health and safety and diverted resources toward this. If that had been done, this would have been far less of an issue. It’s every hospital fending for themselves, because the public health organizations are not providing adequate input and assistance. It’s really the role of public health instead of hospitals to identify and quell threats. Hospitals are great at treating diseases, managing your heart disease and your appendicitis. But we’re not public health organizations and we need them to step up.
— As told to Tara Law